SDK setup for KMP apps
This guide shows the steps to set up the Kotzilla SDK in your KMP app.
Before starting, your application must be registered on the Kotzilla Platform:
- Using the Koin IDE Plugin inside Android Studio or IntelliJ IDEA, or
- Via the Kotzilla Console for a web-based onboarding experience.
Once your app is registered and the type is selected, follow the steps below to integrate the SDK, capture analytics, and start debugging and monitoring your app.
Step 1 - Setup Kotzilla SDK (KMP)
1.1 Kotzilla project configuration file
Download the kotzilla.json configuration file for your shared module and place it in the module directory:
Module (shared module) Gradle file: <project>/<shared module>`
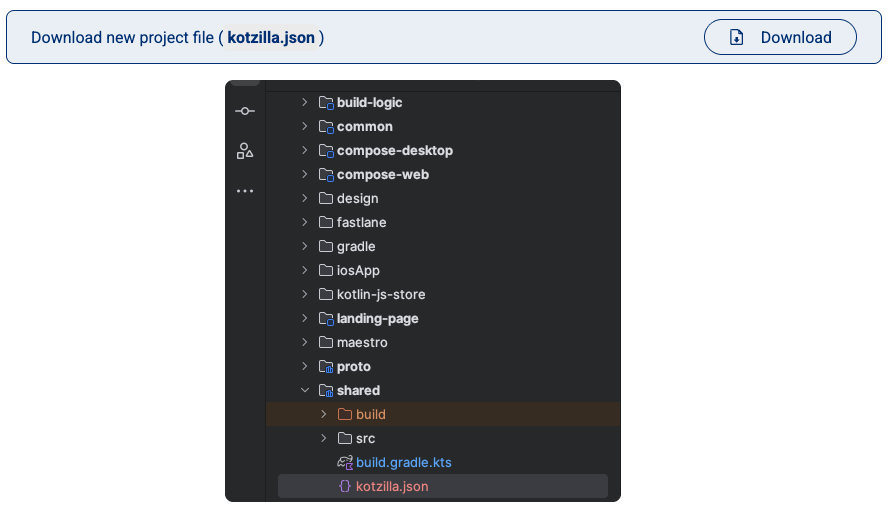
This file contains your API key, version, and SDK configuration for shared code.
1.2 Set up the SDK
The instructions below use Version Catalog configuration by default.
If your project uses the traditional Gradle setup, please check the documentation here for specific instructions.
Kotzilla SDK is available on both Maven Central and the Kotzilla public repository. More information on how to configure access to the Kotzilla repository is available here
Add the following lines to your libs.versions.toml file:
[versions]
kotzilla = "2.0.4" // Check the latest version available below
[libraries]
kotzilla-sdk = { group = "io.kotzilla", name = "kotzilla-sdk", version.ref = "kotzilla" }
[plugins]
kotzilla = { id = "io.kotzilla.kotzilla-plugin", version.ref = "kotzilla" }
Set up the Kotzilla Plugin in your project root-level Gradle file (<project>/build.gradle.kts):
plugins {
alias(libs.plugins.kotzilla) apply false
}
In your shared module Gradle file (<project>/<shared module>/build.gradle.kts), add:
plugins {
alias(libs.plugins.kotzilla)
}
The SDK dependency is automatically added to commonMain. No manual implementation line needed.
If you prefer manual control: kotzilla { autoAddDependencies = false } then add:
commonMain.dependencies {
implementation(libs.kotzilla.sdk)
}
1.3 Supported Platforms
The Kotzilla SDK supports these KMP targets:
| Platform | Target | Status | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Android | androidTarget() | Stable | Full crash reporting with mapping file support |
| iOS | iosArm64(), iosX64(), iosSimulatorArm64() | Beta | dSYM setup required for crash symbolication |
| JVM | jvm() | Experimental | Crash reporting works; no mapping file support yet |
- iOS (Beta): Works well, minor issues may exist — feedback welcome
- JVM (Experimental): Crashes captured but obfuscated code shows obfuscated traces
For Compose Multiplatform (which adds JS/WASM browser targets), see CMP Setup.
1.4 Sync Gradle
Sync your project in Android Studio or IntelliJ IDEA to apply the changes.
1.5 iOS Platform Support
The Kotzilla SDK supports iOS platforms in KMP projects.
iOS Build Configuration
Your shared module's build.gradle.kts should already include iOS targets:
kotlin {
// iOS targets
listOf(
iosX64(),
iosArm64(),
iosSimulatorArm64()
).forEach { iosTarget ->
iosTarget.binaries.framework {
baseName = "SharedModule" // Your shared module name
isStatic = true
}
}
// Other KMP targets
androidTarget()
// ... jvm, etc.
}
The Kotzilla SDK will automatically be included in your iOS framework when you build for iOS targets.
Xcode Integration
When integrating the shared KMP module into your Xcode project:
- The Kotzilla SDK is embedded in your shared framework
- No additional iOS-specific configuration is required
- Analytics data is automatically collected when the app runs on iOS
For framework generation, use Gradle tasks like:
Debug builds:
./gradlew linkDebugFrameworkIosSimulatorArm64
./gradlew linkDebugFrameworkIosArm64
./gradlew linkDebugFrameworkIosX64
Release builds:
./gradlew linkReleaseFrameworkIosSimulatorArm64
./gradlew linkReleaseFrameworkIosArm64
./gradlew linkReleaseFrameworkIosX64
1.6 iOS Crash Reporting (Beta)
SDK 2.0.x captures iOS crashes automatically. For readable crash reports, dSYM upload is required.
iOS crash reporting is a beta feature. Your feedback is welcome: contact us.
Without the correct dSYM file, iOS crash reports show only memory addresses — no function names, no file names, no line numbers.
One-Time Setup
Run this command to inject the dSYM upload script into your Xcode project:
./gradlew setupKotzillaXcode
Re-run after SDK updates to refresh the embedded script.
How It Works
- App crashes → crash data saved locally on device
- App relaunches → crash report uploaded to Kotzilla
- dSYM matched → readable stack traces appear in Console
Manual dSYM Upload
If automatic upload fails:
./gradlew uploadDsymFile
Version Consistency Warning
Each version can only have one dSYM file. If you rebuild the same version, the new dSYM overwrites the previous one, making older crashes unreadable.
Critical mistakes to avoid:
- Rebuilding a released version and uploading its dSYM (overwrites production dSYM)
- Using the same version for both debug and release builds
Always increment your version for each release build, including hotfixes.
Disable iOS Crash Reporting (Optional)
monitoring {
onConfig { useIosCrashReport = false }
}
1.7 JVM Target Support (Experimental)
For JVM-only projects (Desktop apps, backend services), add the JVM target:
kotlin {
jvm() // Desktop/server target
androidTarget()
// ... other targets
}
The SDK captures crashes and analytics on JVM with no additional configuration.
Mapping file support is not yet available for JVM. If you use obfuscation (e.g., ProGuard), stack traces will show obfuscated names.
Step 2 - Start Kotzilla SDK (KMP)
Initialize the Kotzilla SDK in your shared module Koin configuration (Koin.kt in commonMain) to capture analytics for multiplatform targets:
import io.kotzilla.generated.monitoring
startKoin {
// Your current Koin configuration
..
// Add Kotzilla monitoring
monitoring()
}
The monitoring() function is generated at build time by the Kotzilla Gradle plugin. It reads the API key and configuration from your kotzilla.json file automatically.
Step 3 - Go To Dashboard
Now that the SDK is configured, you can build and run your app to start capturing data from a first user session.
Once you've stopped the app:
- Click Check your data to confirm everything is being collected correctly.
- Then click Go to Dashboard to view your app’s performance and configuration insights.